Top 4 Viral infections are a significant health concern, often leading to severe coughing episodes that can be distressing and debilitating. This article delves into the various viral infections responsible for severe coughs, their signs and symptoms, and essential protective measures to safeguard against these illnesses.
Viral Infections:
Viral infections causing severe coughs are a common occurrence worldwide, affecting individuals of all ages. These infections can be caused by a variety of viruses, each with its own set of symptoms and complications. Understanding the signs and symptoms of these viral infections is crucial for early detection and appropriate management.

Top 4 Viral Infections Causing Severe Cough:
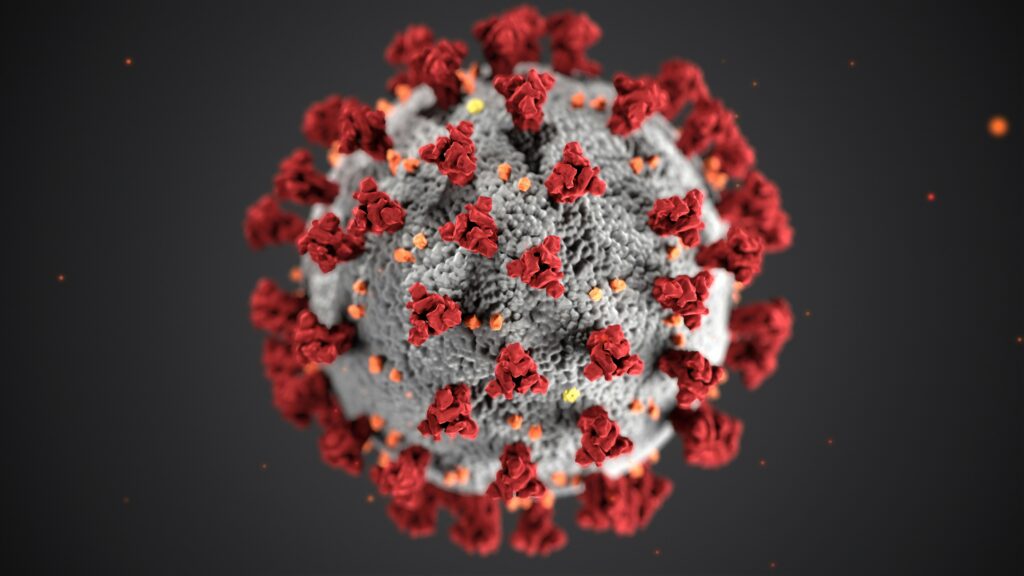
Influenza (Flu):
Influenza viruses are notorious for causing severe respiratory symptoms, including coughing fits. The flu can lead to complications such as pneumonia, especially in vulnerable populations like the elderly and young children.
Morphology:
The influenza virion, or infectious particle, is roughly spherical and enveloped. The outer layer of the virus is a lipid membrane derived from the host cell in which the virus replicates. Embedded in this lipid membrane are proteins known as hemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA), which are crucial for determining the subtype of the influenza virus.

Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV):
RSV is a common cause of respiratory infections in infants and young children, often presenting with severe coughing spells. Severe cases may require hospitalization.
Morphology:
Respiratory Syncytial Virus (RSV) is a pleomorphic enveloped RNA virus belonging to the Pneumoviridae family. The virus exhibits three distinct morphological categories: spherical, asymmetric, and filamentous. Studies have revealed that RSV particles are filamentous across various virus strains and cell lines, with filament lengths ranging from 0.5 to 12 μm and an average diameter of approximately 130 nm.
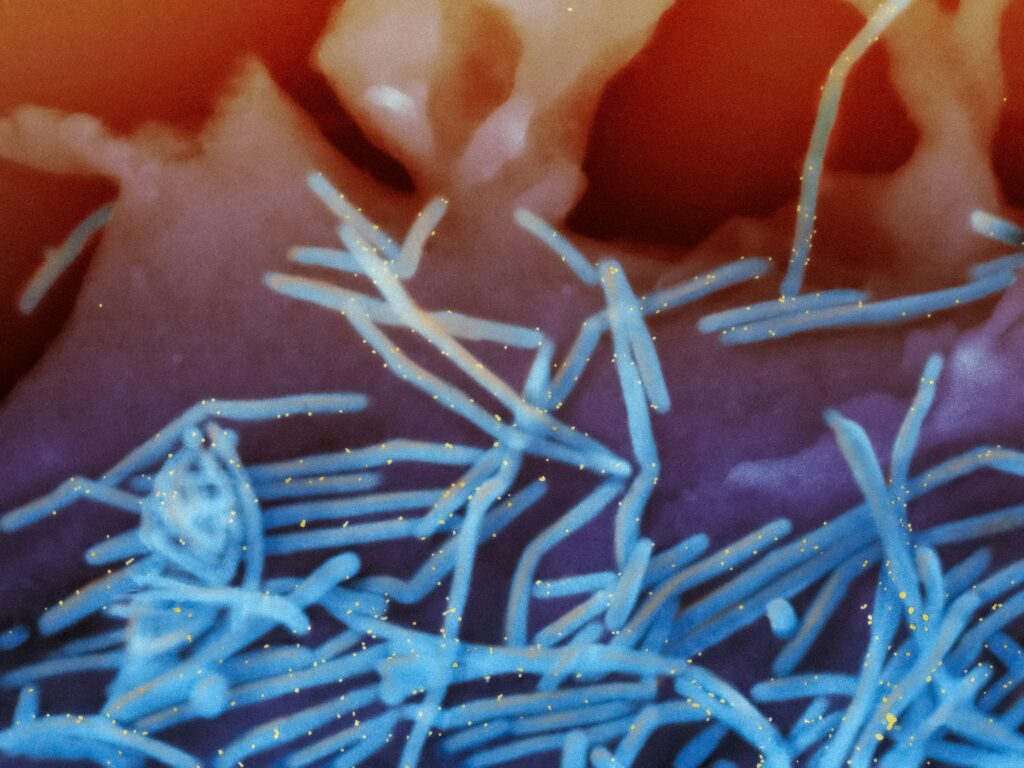
Adenovirus:
Adenoviruses can cause a range of respiratory illnesses, including bronchitis and pneumonia, leading to persistent coughing and respiratory distress.
Morphology:
The morphology of adenoviruses is characterized by their medium-sized (90-100 nm), nonenveloped structure with an icosahedral nucleocapsid containing a double-stranded DNA genome.
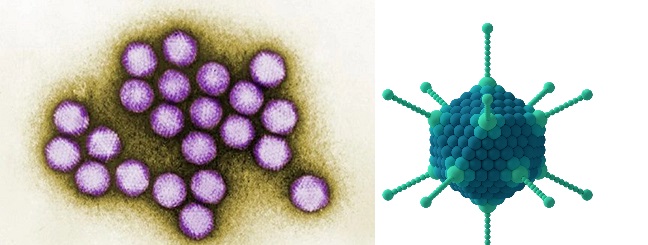
Parainfluenza Virus:
Parainfluenza viruses are known to cause croup in children, characterized by a barking cough and difficulty breathing.
Morphology:
The morphology of the parainfluenza virus is characterized by pleomorphic virions containing single-stranded negative-sense RNA, with diameters ranging from 150 to 200 nm. These virions are enveloped and contain structural proteins like hemagglutinin-neuraminidase (HN) and fusion protein (F) that play essential roles in attachment, cell entry, and fusion processes.
Signs and Symptoms
Persistent Cough:
A hallmark symptom of viral infections is a persistent cough that may be dry or produce phlegm.
Fever:
Many viral infections are accompanied by fever, which can indicate an active immune response.
Sore throat:
Irritation in the throat is common with viral respiratory infections.
Fatigue:
Viral illnesses can cause extreme fatigue due to the body’s efforts to fight off the infection.
Shortness of Breath:
Severe coughing episodes can lead to difficulty breathing, requiring immediate medical attention.
Protective Measures
Hand Hygiene: Regular hand-washing with soap and water can prevent the spread of viruses.
Vaccination: Getting vaccinated against influenza and other preventable viral infections can reduce the risk of severe illness.
Avoiding Close Contact: Limiting contact with individuals who are sick can help prevent the spread of viruses.
Covering Mouth and Nose: When coughing or sneezing, covering your mouth and nose with a tissue or elbow can prevent the spread of droplets containing viruses.
Stay Home When Sick: If you are experiencing symptoms of a viral infection, stay home to prevent spreading the illness to others.
Conclusion
In conclusion, viral infections causing severe coughs can have significant implications for individual health and public well-being. By recognizing the signs and symptoms early on and adopting preventive measures, we can mitigate the impact of these infections on our communities. Stay informed, practice good hygiene, and seek medical attention when necessary to protect yourself and those around you from the menace of viral respiratory illnesses.
https://blogs92.com/wp-admin/post.php?post=147&action=edit

Wow, that’s what I was seeking for, what a material! present here at this weblog, thanks admin of this web page.